Mar 04, 2016 To easily run the Disk Cleanup tool, launch File Explorer, select This PC, and select Local Disk (C:). To continue, select the Drive Tools Manage tab and click the Cleanup button, as shown in. In the search box on the taskbar, type disk cleanup, and select Disk Cleanupfrom the list of results. Select the drive you want to clean up, and then select OK. Under Files to delete, select the file types to get rid of. To get a description of the file type, select it. Mar 30, 2019 Disk Cleanup is the Windows’ equivalent of spring cleaning. Essentially, it walks through your cluttered home (the hard drive of your PC) with a trash bag and recommends items you should toss out. It picks the ones that you don’t use and won’t miss. Some of these files include. Launches the Disk Cleanup Tool for drive c. The switch /LOWDISK is used when a disk drive is running low in disk space. When launched, Disk Cleanup tool opens with all checkboxes checked by default. Cleanmgr.exe /lowdisk /d c. The command will launch Disk Cleanup tool against the drive c with all checkbox checked by default.
The built-in Windows tool, Disk Cleanup, which can be launched as cleanmgr.exe from the Run dialog, supports a number of interesting command line arguments which can be useful in various situations. Let's review them and see how you can use them.
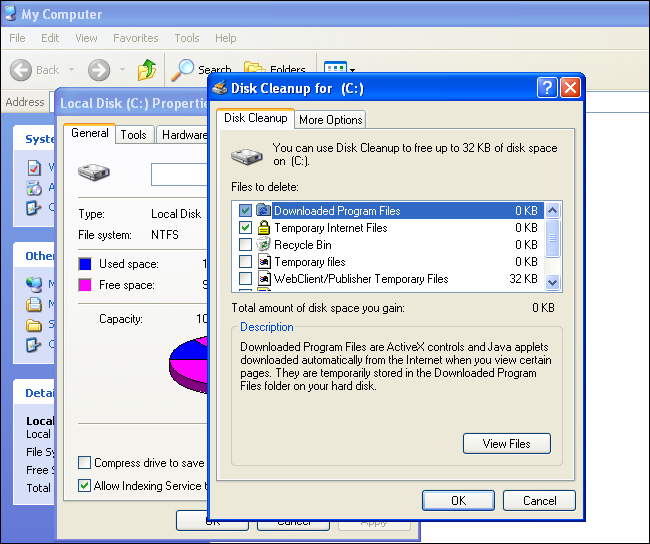 You can learn the switches available for Disk Cleanup by entering the following command in the Run dialog:
You can learn the switches available for Disk Cleanup by entering the following command in the Run dialog:See the following screenshot:
The list is as follows:
Here's what those switches mean.
cleanmgr.exe /D DRIVELETTER
Executes disk cleanup for a specific drive. The user should specify the drive letter without ':' as shown below:
The command above will launch disk cleanup for drive C:.
You can combine the /D argument with other switches of cleanmgr.exe.
cleanmgr.exe /SAGESET
The SAGESET key allows you to create a preset of selected checkboxes in cleanmgr.exe. Once this is done, you can launch the preset using the /SAGERUN option. The syntax is as follows:
The command needs to be executed elevated (as administrator).
Where 'number' can be any value from 0 to 65535. The options you select during the SAGESET session will be written to the Registry and stored there for further use. The command needs to be executed elevated.
Use it as follows:
- Open an elevated command prompt.
- Type the following command
Suppose you use the number 112, for example:
- Tick the options you want to be enabled for this preset as shown below:
- Click OK to save the preset under the number you entered in the Run dialog.
Since you started cleanmgr.exe /SAGESET:n elevated, it will be opened directly in the 'Clean up system files' mode. See the following article: How to run Disk Cleanup directly in the system files mode and speed it up.
Technically, every checkbox shown in Disk Cleanup reflects the appropriate registry subkey under the following Registry branch:
For example, the Windows Upgrade Log Files subkey reflects the same option in the user interface of the app.
For every value you check, it will be marked under the StateFlagsNNNN DWORD value, where NNNN is a number you passed to the SAGESET argument. I have the value StateFlags0112 there for my /SAGESET:112 command:
cleanmgr.exe /SAGERUN
The argument /SAGERUN allows the user to launch the preset configured earlier with the /SAGESET:n command. The syntax is as follows:
Use the same number that you used for the previous /SAGESET:number command.
Combining with the previous example, you should do the following.
- Open an elevated command prompt.
- Type the following command
Suppose you use the number 112, for example:
- Tick the options you want to be run for this preset as shown below:
- Click OK to save the preset under number 112.
- Now, type cleanmgr.exe /SAGERUN:112 in the Run dialog. It will start clean up using the preselected options automatically.
The cleanup process will be started immediately, without any confirmation prompt. Disk Cleanup will also be closed automatically.
If the /D argument is not specified for this command, it will be applied to all drives.
You can see the article How to run Disk Cleanup directly in the system files mode and speed it up.
The following commands are not documented. To discover them, I used Sysinternals Process Monitor and logs of the cleanmgr utility. If they don't behave as described, please correct me in the comments.

cleanmgr.exe /TUNEUP
The command is similar to the described SAGESET functionality. In Windows 10, it does exactly the same thing. Like the SAGESET switch, it writes presets to the Registry. It can be used instead of SAGESET. The syntax is as follows:
The command needs to be executed elevated.
If you previously configured the number specified with the TUNEUP switch with SAGESET, it will reflect the changes you made:
This switch is not documented, so Microsoft can remove or change its behavior at any moment. I recommend you to use SAGESET instead.
cleanmgr.exe /LOWDISK
This switch is used when Windows notifies the user that he is running out of disk space on a drive. When you click the notification, Disk Cleanup opens with all checkboxes checked by default. You can execute it from the Run dialog as follows:
See the following screenshot:
Once you press the Enter key, it will analyze the drive and show the familiar user interface, but with all checkboxes checked by default:
You can run the command from an elevated command prompt to make it switch to the system files mode.
cleanmgr.exe /VERYLOWDISK
It is the same as the /LOWDISK disk switch, but it will cleanup all files automatically. It won't show you a confirmation, but will show you a dialog to indicate how much free disk space you have now.
Syntax:
Run the command from the elevated command prompt to make it switch to the system files mode.
cleanmgr.exe /SETUP
The setup switch analyzes the system files left from a previous Windows version. For example, if you upgraded from Windows 7 to Windows 10, running this switch is useful. It also needs to be executed from an elevated command prompt:
The application will calculate the space used by files from the previous Windows installation. It is similar to the cleaning Previous Windows Installation files using the user interface of Disk Cleanup in regular mode. The application will analyze the following locations:
The application will not clean them up automatically. It won't show a user interface either. Instead it will write two log files which you can inspect:
cleanmgr.exe /AUTOCLEAN
It's the same as above, but the application will remove files from the previous Windows installation or the previous in-place upgrade automatically.
The following folders will be removed:
The application will write the results to the following log files:
No user interface will be shown.
The syntax is as follows:
The command needs to be executed elevated, e.g. you need to launch it from an elevated command prompt instance.
That's it.
Don't forget to tell us if some commands don't behave as described for you. Feel free to leave a comment if you have a question or a suggestion.
Advertisment
Are you running out of your Disk Space? Have you upgraded to Windows 10? Are you storing hundreds of HD quality movies, “n” number of high-resolution photos, thousands of songs then sure you would have already hit the upper limit of your disk space storage capacity? So, you would be worried how to clean disk space capacity in your Windows 10.
This is quite a common issue that almost everyone is facing in today’s digital world. Even if drives are bigger than earlier times and at a lesser price but still we keep running low on disk space. Moreover, with Microsoft’s aggressive update strategy and low requirements of Windows 10 system has enabled even the older machines that have less amount of space as compared to modern models to upgrade to Windows 10.
However, whatever may be the reason for you approaching the upper limit of your disk space capacity, your first step should not be to simply go and buy a new drive. Instead, your first approach should be to make optimum use of your disk space. This can be achieved by removing files, apps, and games that you are not using anymore.
Here are ways to restore your storage space back on your Windows 10 PC.
1. Delete older versions of Windows
Windows by default save the data from the older versions of Windows post up gradation. This is so as to facilitate you to get back to your older version whenever you feel to do so. But this old data utilizes a lot of space. Not only the older versions but Windows also automatically saves files while installing the latest Anniversary update. It is quite easy to delete these files. Here is how to do it:
- Go to the Settings app.
- Select Storage in System.
- Select primary storage.
- A list of different categories will be displayed with a list of space they are using.
- Click on temporary files. Here mark the checkbox beside “Previous Versions of Windows” and click on Remove files.
2. Clean the Recycle Bin
Disk Cleanup On Windows 10 Hp
Whenever you delete any file or folder or photos in your PC, they are deleted from that space but are stored in Recycle Bin in case if required again. However, they occupy your crucial disk space. To empty the Recycle Bin, simply
- Right-click on your Recycle Bin.
- A drop-down menu will be displayed. Click on Empty Recycle bin.
- A dialogue box asking if you permanently wish to delete these items will be displayed on your screen
- Click “Yes” to delete them permanently.
Disk Cleanup On Windows 10 Hp
3. Clean the Update Cache
The copies of the Update installation files are stored in the Update Cache. In case, when you are forced to reapply an update, it can use the saved one. However, they take up space of your disk. In order to clean the disk space first stop the Windows Update Service:
- Search Services in the taskbar.
- Right click on it and a drop-down menu will be displayed.
- Click on Run as an administrator.
- From the list select Windows Update and right click on it.
- On the displayed menu click on Stop.
Disk Cleanup On Windows 10
We have successfully stopped the Windows Update Service. Now, we need to delete the files.
- Now, Click Windows +R to open the run box.
- Type C:WindowsSoftwareDistributionand press Enter.
- You can delete everything displayed in the download folder.
- Now, go back to services and re-enable the Windows Update.
This method also enables you to remove corrupt files.
4. Disable Hibernation
Hibernation allows you to conserve power when you are not using your Windows machine. Sleep also does that. But the difference in both is that Sleep mode saves all your open documents and running applications in RAM, while Hibernate saves it all to the hard disk. Hibernate thus, saves the content of your PC in the disk so that you can shut down your PC completely and still your current data will be safe. In spite of its good use, it consumes several gigabytes of space to save the content in RAM to the hiberfil.sys file on the hard drive. In fact, if you don’t use Hibernate mode simply delete it. As deleting it will by default also delete all the data that is saved from earlier hibernations.
To clean disk space, you need to disable hibernation to delete the hibernated data that is occupying space in your disk. To do so,
- Open Start and search Command Prompt.
- Right-click on it and select Run as an administrator.
- Type on it powercfg /hibernate off
- This will also turn off your ability to use Hibernation. However, when you have low space on your disk and you need space immediately, this is the good option.
- However, if ever you wish to turn it on repeat the above steps and type exe -h on instead.
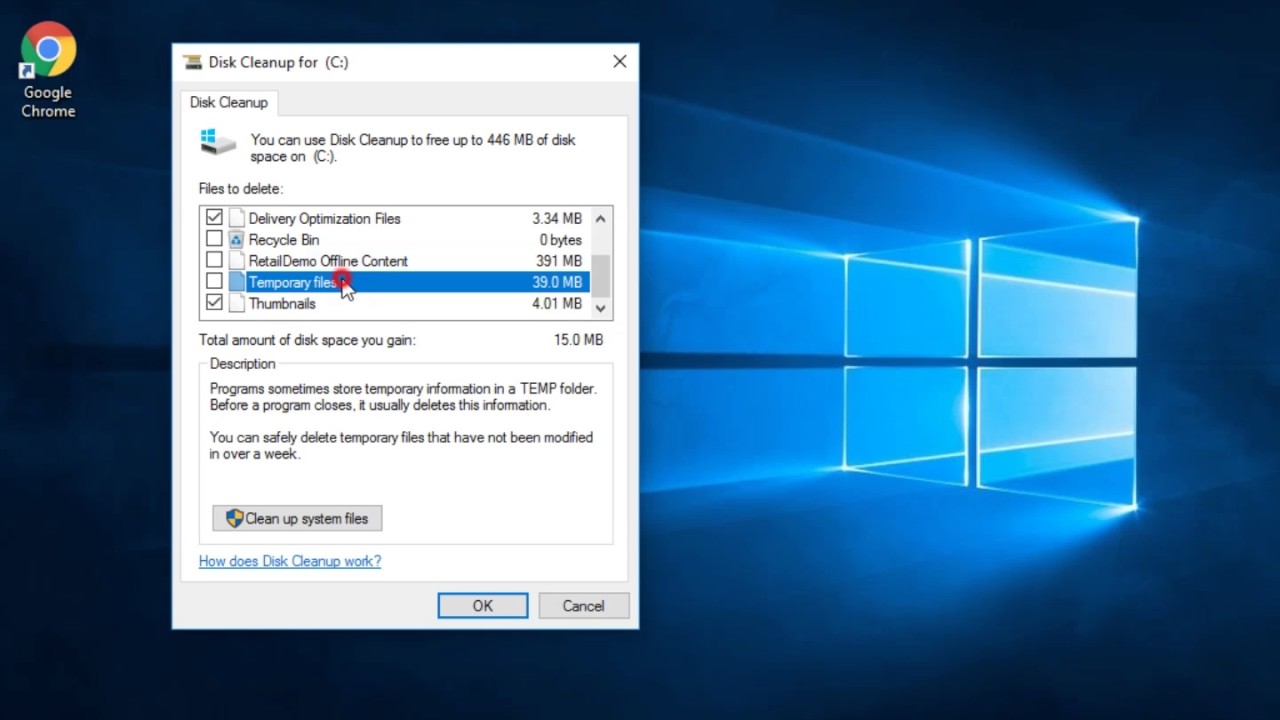
5. Delivery Optimization Files
Delivery Optimization is a new feature of Windows 10. It enables your device to pull updates from other machines nearby. The motto behind it is to deliver the updates faster. However, there are complains that it is using higher bandwidth and occupies a bigger chunk of memory.
The earlier files can be easily deleted and also disable this option so new files don’t keep on taking more space. Here is a step by step process to clean disk space:
- In Windows taskbar go to Settings.
- Click on Update & Security
- Select Advanced Options.
- Choose How Updates Are Delivered.
- Turn it off.
Head to Start > Settings > Update & Security > Advanced Options > Choose How Updates Are Delivered. Once there, make sure the slider is set to the Off position.
Now to clean the space,
- Search Disk Clean-up and open the app.
- A dialogue box will be displayed asking you to select the drive you want to clean and click OK.
- A list of files that can be removed will be displayed. Search for Delivery Optimization files in the list and check the box beside it. Click OK. Windows will automatically delete it.

6. OEM Recovery Partition
Windows 10 also has OEM Recovery Partition. They are not much required and so can be removed safely. But it requires creating a recovery drive. Creating a recovery drive implies the need of a USB stick.
In order to create a drive,
- Type in the Taskbar – Create a Recovery Drive.
Follow the instructions as displayed on your screen. Insert a USB drive when asked. Once the process is finished, you’ll see the option to delete the recovery partition from your PC on the final screen. Click the link and choose Delete to proceed.
7. Recovery Partition
Once you off this option, you would neither be able to use the Windows 10’s recovery options nor will you be able to boot into the recovery environment to troubleshoot other aspects of the operating system. Moreover, before initiating this process, have the backup ready for all your data and even create a USB recovery drive.
Once you are done with it, you can start the process.

- Search Command Prompt in the taskbar.
- Right click on it and click on Run as administrator.
- Type Diskpart and Press Enter.
- Now type List disk and again press Enter.
- Type Select disk _ (in blank write the number of the disk where your recovery partition is saved.) Then type List Volume.
- A list of all the volumes on the disk will be displayed. Along with it, your recovery partition will also be displayed.
- Now type Select Volume 3 (here I have written 3 as that is my recovery portion. You write your recovery portion number.)
- Type Delete Volume and press Enter.
Unused apps and games
Many apps and games came preinstalled on your computer and you may not be using them all. Deleting such apps may clean disk space on your device. Or even games or apps that you may have installed and you don’t use them now. But they eat up a lot of storage place.
Here is a detailed process to remove them from your device:
- Go to Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Select Apps and Features.
- Choose the game or app you wish to remove and click on Uninstall button.
Do this process for all the apps and games to clean disk space and you may have enough free space in your Windows 10 laptop.
